Portfolio
What is a portfolio ?
A stock portfolio is a collection of stocks. A stock portfolio can include stocks from a variety of industries and sectors.
In general , it can be a collection of stocks, mutual funds, bonds, ETFs, and other investment vehicles. It is often used as a tool for diversification and risk management.
In short, it’s a mix of different investment assets to achieve the investment objectives of an investor.
Example
George understood the techniques of buying valuable companies at fair prices and now had 7-10 different stocks in his folder. He could not manage more stocks, so he decided to invest in ETFs to take advantage of entire indices rather than investing in any particular stocks.
He also wanted to maintain financial discipline by investing a fixed amount every month in a specific set of stocks; thus, he invested in Mutual funds. To balance the risk of his investments, he also invested some amount in bonds, yielding him a fixed return at low risk.
So, George created a basket of investments that included securities like stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, and bonds. The basket of securities according to one’s risk and return appetite is called Portfolio.
Why Portfolio ?
By spreading your investments across various types of assets and markets, you can reduce the risk of catastrophic financial losses. Different investment assets perform differently at any given point in time, and holding a mix helps to mitigate the impact of a drop in any one of them.
For example, during a recession, if your stocks go down, the stability of the bonds and gold in your folder can still provide support.
Portfolio Diversification:
Portfolio diversification balances your portfolio’s risk and return by investing across equity, debt, mutual fund, insurance, etc. The benefit of portfolio diversification is
- Guards the principal amount from substantial market swings
- Reduces the impact of market volatility
- Reduces the huge risk exposure and average out losses from fixed income securities
- Gives peace of mind.
Portfolios Diversification Criteria
The criteria for portfolio diversification can vary depending on the investor’s individual circumstances, but generally include:
- Age: An investor’s age plays a most important role in their portfolio diversification strategy. Younger investors may have more time and be more willing to take on risk for higher returns, while older investors may have a shorter investment period and focus more on maintaining their capital.
- Financial goals: An investor’s financial goals can help to determine their investment strategy and the types of assets they should hold in their portfolio. For example, someone saving for retirement in 20 years may have a different investment strategy than someone saving for a down payment on a house in 2 years.
- Risk tolerance: The question is, will you sell your investment if there is a recession? A more risk-averse investor may choose to hold a higher percentage of bonds or other fixed-income assets in their portfolio, while a more risk-tolerant investor may hold a higher percentage of stocks.
- Expected returns: An investor’s expected returns can help to determine the types of assets they should hold in their portfolio. An investor with a high expected return may choose to hold a higher percentage of stocks or other higher-risk assets in their portfolio, while an investor with a lower expected return may choose to hold a higher percentage of bonds or other lower-risk assets.
- Management fee: The management fee of an investment product, such as a mutual fund or ETF, can impact the overall performance of a portfolio. Investors should consider the investment’s management fee & expense ratio while making decisions. Some mutual funds in the market take 3% free and give 5% returns. But investors are still investing in them.
5 Types of Portfolios
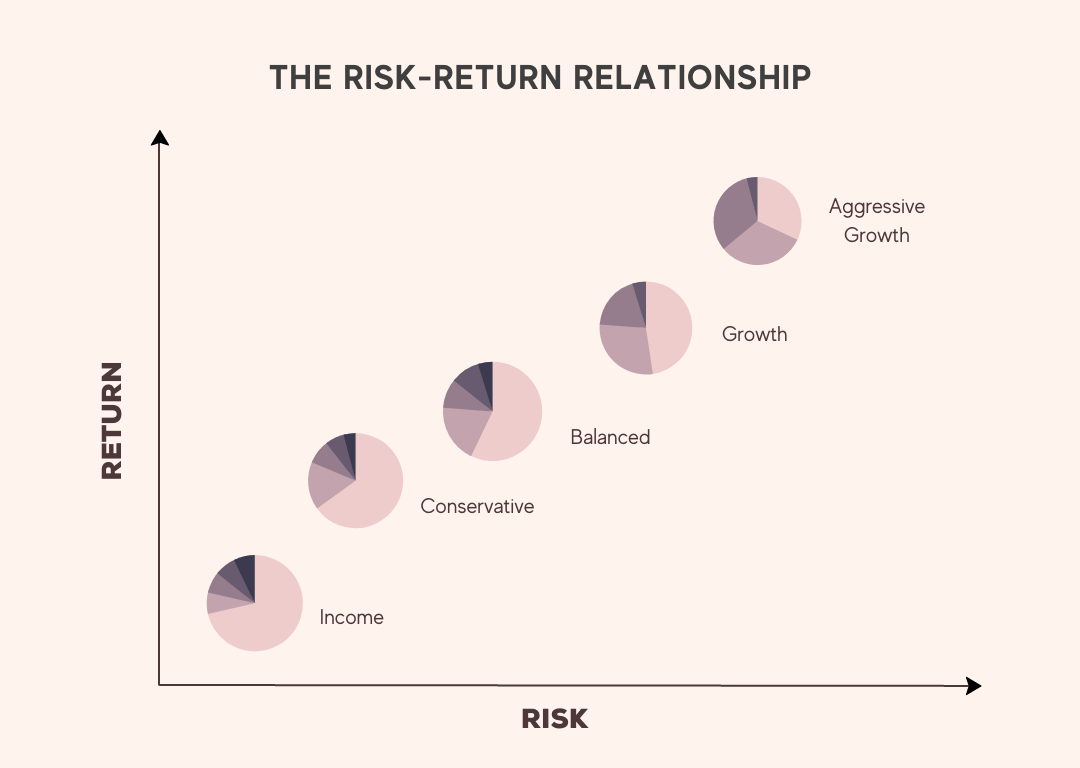
- Aggressive growth portfolio: high-risk, high-return, consists of more stocks and fewer bonds.
- Growth portfolio: designed for capital appreciation over the long term, including growth stocks and mutual funds.
- Balanced portfolio(Hybrid): a blend of both capital appreciation and income, consisting of both stocks and bonds for a moderate level of risk and return.
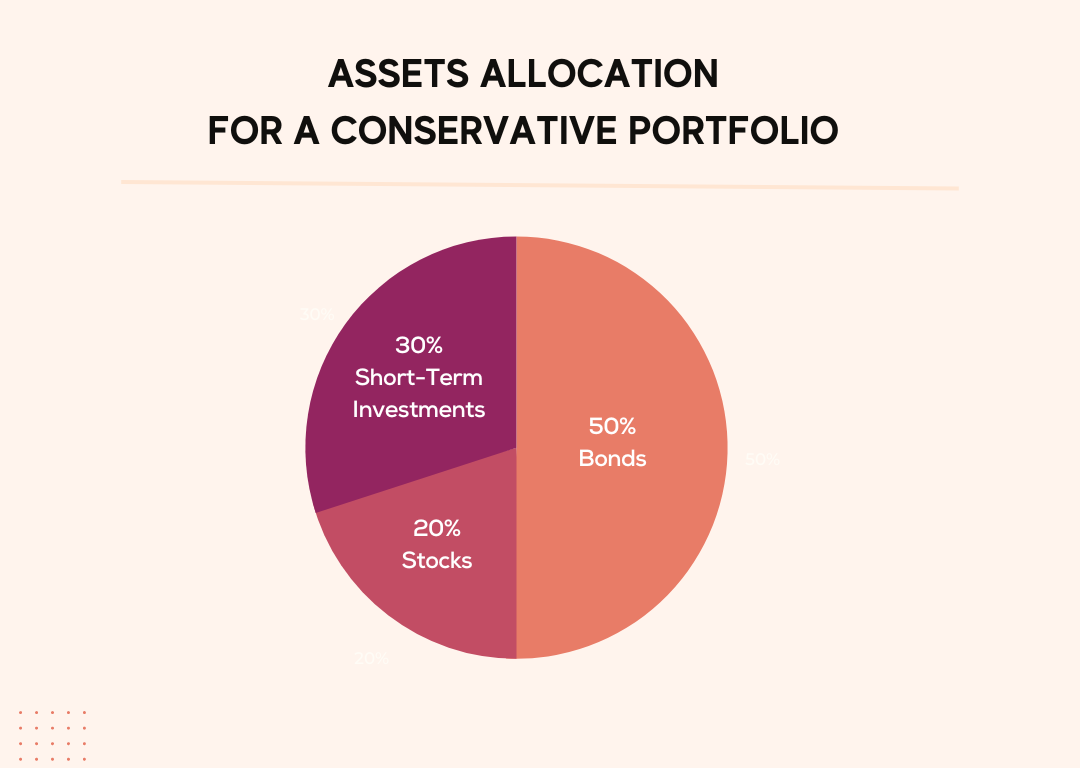
- Conservative portfolio: low-risk, steady income, more bonds, and fewer stocks.
- Income portfolio: designed for a regular income stream, includes bonds, dividend-paying stocks, and REITs.
For example
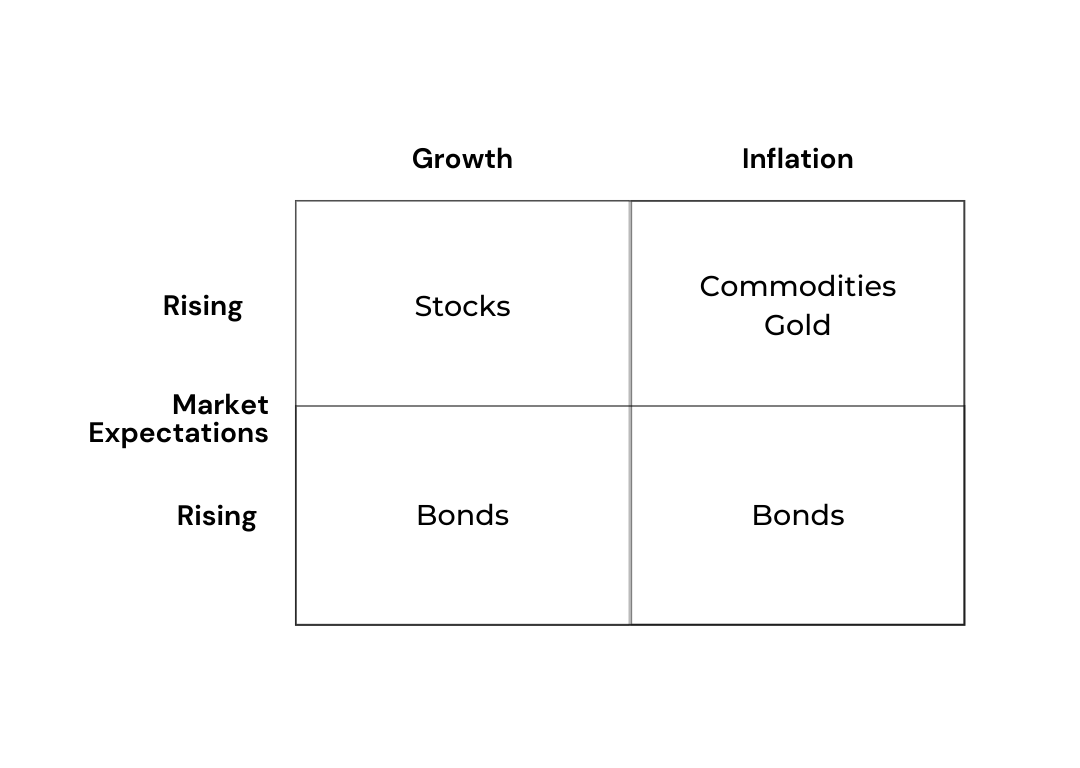
Ray Dalio’s All Weather Portfolio is a famous example of a diversified investment. The All-Weather is designed to perform well in any economic environment, whether during economic growth, inflation, or recession.
What is a portfolio ?
A stock portfolio is a collection of stocks. A stock portfolio can include stocks from a variety of industries and sectors.
In general , it can be a collection of stocks, mutual funds, bonds, ETFs, and other investment vehicles. It is often used as a tool for diversification and risk management.
In short, it’s a mix of different investment assets to achieve the investment objectives of an investor.
Example
George understood the techniques of buying valuable companies at fair prices and now had 7-10 different stocks in his folder. He could not manage more stocks, so he decided to invest in ETFs to take advantage of entire indices rather than investing in any particular stocks.
He also wanted to maintain financial discipline by investing a fixed amount every month in a specific set of stocks; thus, he invested in Mutual funds. To balance the risk of his investments, he also invested some amount in bonds, yielding him a fixed return at low risk.
So, George created a basket of investments that included securities like stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, and bonds. The basket of securities according to one’s risk and return appetite is called Portfolio.
Why Portfolio ?
By spreading your investments across various types of assets and markets, you can reduce the risk of catastrophic financial losses. Different investment assets perform differently at any given point in time, and holding a mix helps to mitigate the impact of a drop in any one of them.
For example, during a recession, if your stocks go down, the stability of the bonds and gold in your folder can still provide support.
Portfolio Diversification:
Portfolio diversification balances your portfolio’s risk and return by investing across equity, debt, mutual fund, insurance, etc. The benefit of portfolio diversification is
- Guards the principal amount from substantial market swings
- Reduces the impact of market volatility
- Reduces the huge risk exposure and average out losses from fixed income securities
- Gives peace of mind.

Portfolios Diversification Criteria
The criteria for portfolio diversification can vary depending on the investor’s individual circumstances, but generally include:
- Age: An investor’s age plays a most important role in their portfolio diversification strategy. Younger investors may have more time and be more willing to take on risk for higher returns, while older investors may have a shorter investment period and focus more on maintaining their capital.
- Financial goals: An investor’s financial goals can help to determine their investment strategy and the types of assets they should hold in their portfolio. For example, someone saving for retirement in 20 years may have a different investment strategy than someone saving for a down payment on a house in 2 years.
- Risk tolerance: The question is, will you sell your investment if there is a recession? A more risk-averse investor may choose to hold a higher percentage of bonds or other fixed-income assets in their portfolio, while a more risk-tolerant investor may hold a higher percentage of stocks.
- Expected returns: An investor’s expected returns can help to determine the types of assets they should hold in their portfolio. An investor with a high expected return may choose to hold a higher percentage of stocks or other higher-risk assets in their portfolio, while an investor with a lower expected return may choose to hold a higher percentage of bonds or other lower-risk assets.
- Management fee: The management fee of an investment product, such as a mutual fund or ETF, can impact the overall performance of a portfolio. Investors should consider the investment’s management fee & expense ratio while making decisions. Some mutual funds in the market take 3% free and give 5% returns. But investors are still investing in them.
5 Types of Portfolios

- Aggressive growth portfolio: high-risk, high-return, consists of more stocks and fewer bonds.
- Growth portfolio: designed for capital appreciation over the long term, including growth stocks and mutual funds.
- Balanced portfolio(Hybrid): a blend of both capital appreciation and income, consisting of both stocks and bonds for a moderate level of risk and return.
- Conservative portfolio: low-risk, steady income, more bonds, and fewer stocks.
- Income portfolio: designed for a regular income stream, includes bonds, dividend-paying stocks, and REITs.
For example
Ray Dalio’s All Weather Portfolio is a famous example of a diversified investment. The All-Weather is designed to perform well in any economic environment, whether during economic growth, inflation, or recession.

