Types of Stocks
Explore the types of stocks for investment, like cyclical, income, growth, and value stocks. Discover the benefits of each type to make informed investment decisions.
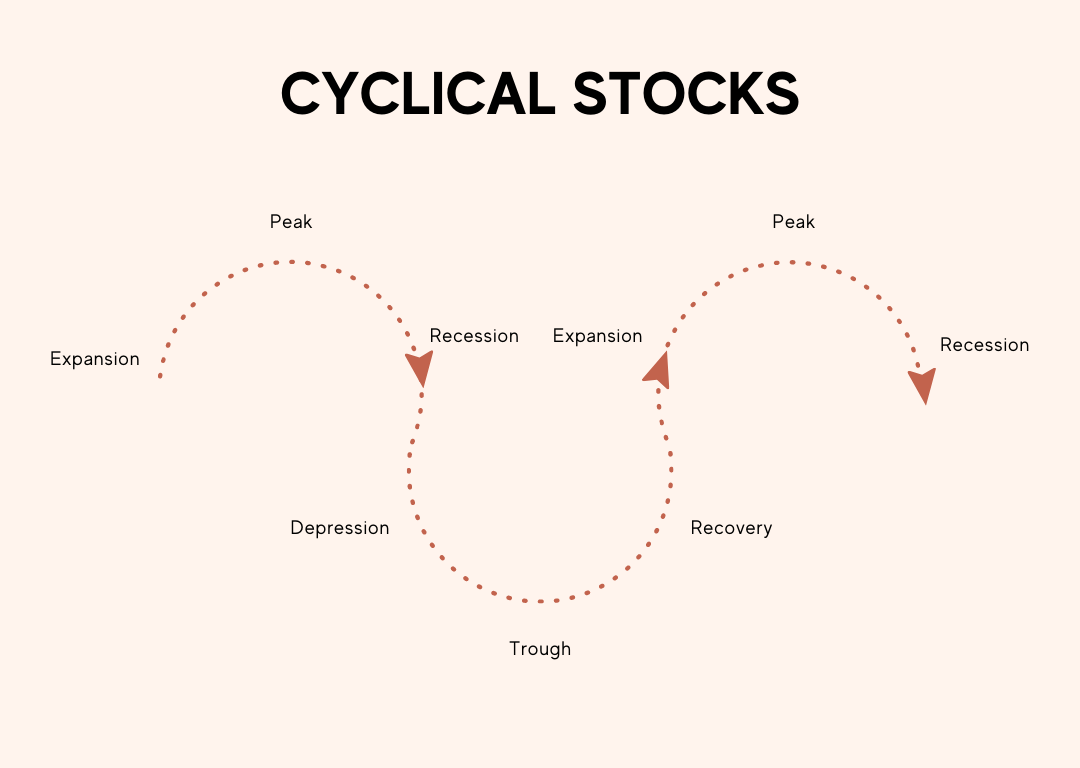
Cyclical Stocks
Cyclical stocks are companies whose performance is closely tied to the overall business cycle.
When the economy is doing well, cyclical stocks perform strongly as consumers and businesses increase spending, which drives demand and prices. On the other hand, when the economy has challenges, cyclical stocks tend to underperform as consumers and businesses reduce their spending.
Example
Stocks in the housing, financial services, automotive industry, and consumer durables are perfect examples.
Four Basic Stages:
- Expansion: Economic growth starts to increase. Employment and production pick momentum. Usually, there is monetary stimulus from the government. The stock price rises due to the growing demand for the product. A period of sustained growth.
Expansion → Increased Economic Output + Consumer Spending Increases + Stock Prices Rises
- Peak: This is the time when the business is at the peak of its production. Economic growth slows or stagnates. Govt starts fiscal and monetary restrictions. In this phase, the price of the stock is at its peak.
Peak →Slow Economic Growth + Consumer Spending Decreases + Stock Price Peaked
- Recession: This is a period of economic downfall. During a recession, cyclical stocks can experience significant declines as the demand for products and services evaporates. Stock price starts falling.
Recession → Lower Economic Output + Consumer Spending Decreases + Stock Price Falls
- Trough: This is the lowest point for any business when there is enough supply of product but no demand. The stock price is at its lowest level. In response, the government may implement fiscal policies to stimulate the economy. It’s a transitional period when the economic decline stops and recovery begins.
Trough → No Growth + No Spending + Stock Price Bottomed
Income Stocks

Income stocks are the stocks that provide regular income in the form of dividends to their investors. These businesses distribute a portion of profits to its shareholders. These companies are often mature, well-established, and have a stable track record of profitability.
Characteristics of income stocks:
- Purpose: Regular passive income.
- Cashflows are reliable and predictable.
- These stocks have low exposure to risk.
- These stocks give moderate returns over the year.
- The pace of growth is low-moderate.
- Consistent increase in dividend payouts
Example
Coca-Cola (KO) – The company has paid dividends to its investors for over 100 years.
Value Stocks
Value stocks are shares in companies considered undervalued by the market. These companies usually have a low price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio or price-to-book (P/B) ratio, indicating that the stock is priced lower than its intrinsic value.
Characteristics of value stocks:
- In this investment strategy, an investor buys a high-quality stock at a lower price than its intrinsic value.
- The stocks provide a margin of safety
- These stocks have solid fundamentals and promising numbers, making them investors friendly.
- Usually called bargained prices
- Most likely pay dividends
- High research required
Growth Stocks

Growth stocks are shares of companies that are expected to grow faster than the overall market.
A company uses its profit for two purposes.
- Distributes to its shareholder as a dividend or
- Retains these earnings for re-investment in the company.
Usually, stocks of companies that re-invest all or most of their profit in the company’s progress are called growth stocks.
Characteristics of growth stock:
- These stocks focus more on the expansion and growth of the company. The growth of these companies is faster than the average growth of other companies in the same industry.
- The risk involved in these stocks is high
- If the stock performs well, they yield excellent returns to investors leading to massive wealth accumulation.
- Growth stocks have high price-to-earnings ratios (P/E ratios) because investors are willing to pay more for the potential of future earnings growth.
- Growth stocks are more volatile
Example
Amazon re-invests its profits for growth and expansion. Thus, it is categorized into growth stocks.
Blue Chip Stock
Blue chip stocks are shares of large, well-established companies with a long history of reliable earnings and stable growth. These companies are typically leaders in their industry and have a reputation for consistent performance.
Characteristics of blue chip companies:
- They have a long history of operations
- Stocks are financially strong
- Generally, they have a large market capitalization
- The companies are known for offering high-quality products and services
- They are often market leaders
Example
Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) – A healthcare company that develops, manufactures and sells pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and consumer healthcare products.
The S&P 500 includes many blue chip companies, as they are typically large,
Sector Stocks
Every stock belongs to a particular sector. A sector is a grouping of companies involved in similar types of businesses, such as technology, healthcare, energy, or consumer goods.
The GICS framework
The GICS (Global Industry Classification Standard), is a system developed by MSCI. The GICS structure comprises 11 sectors, 24 industry groups, 69 industries, and 158 subindustries.
Here are some examples of companies that fall under 11 sector stocks:
Communication services:
- Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL)
- Facebook Inc. (FB)
- Netflix Inc. (NFLX)
- Walt Disney Co. (DIS)
Consumer discretionary:
- Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN)
- Nike Inc. (NKE)
- Starbucks Corp. (SBUX)
- Tesla Inc. (TSLA)
Consumer staples:
- Coca-Cola Co. (KO)
- Procter & Gamble Co. (PG)
- Walmart Inc. (WMT)
- McDonald’s Corp. (MCD)
Energy:
- Chevron Corp. (CVX)
- Exxon Mobil Corp. (XOM)
- ConocoPhillips (COP)
- Schlumberger Ltd. (SLB)
Financials:
- JPMorgan Chase & Co. (JPM)
- Bank of America Corp. (BAC)
- Wells Fargo & Co. (WFC)
- Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (BRK.A)
Health care:
- Johnson & Johnson (JNJ)
- Pfizer Inc. (PFE)
- UnitedHealth Group Inc. (UNH)
- AbbVie Inc. (ABBV)
Industrials:
- Boeing Co. (BA)
- General Electric Co. (GE)
- Honeywell International Inc. (HON)
- 3M Co. (MMM)
Information technology:
- Apple Inc. (AAPL)
- Microsoft Corp. (MSFT)
- Intel Corp. (INTC)
- Advanced Micro Devices Inc. (AMD)
Materials:
- Dow Inc. (DOW)
- Ecolab Inc. (ECL)
- DuPont de Nemours Inc. (DD)
- Freeport-McMoRan Inc. (FCX)
Real estate:
- American Tower Corp. (AMT)
- Prologis Inc. (PLD)
- Simon Property Group Inc. (SPG)
- AvalonBay Communities Inc. (AVB)
Utilities:
- NextEra Energy Inc. (NEE)
- Dominion Energy Inc. (D)
- Duke Energy Corp. (DUK)
- Southern Co. (SO)
Who can Invest in sector stocks?
- Investors who have done extensive research on particular sectors and stocks of these sectors
- Investors who can predict and estimate future sectoral demand.
Explore the types of stocks for investment, like cyclical, income, growth, and value stocks. Discover the benefits of each type to make informed investment decisions.

Cyclical Stocks
Cyclical stocks are companies whose performance is closely tied to the overall business cycle.
When the economy is doing well, cyclical stocks perform strongly as consumers and businesses increase spending, which drives demand and prices. On the other hand, when the economy has challenges, cyclical stocks tend to underperform as consumers and businesses reduce their spending.
Example
Stocks in the housing, financial services, automotive industry, and consumer durables are perfect examples.
Four Basic Stages:
- Expansion: Economic growth starts to increase. Employment and production pick momentum. Usually, there is monetary stimulus from the government. The stock price rises due to the growing demand for the product. A period of sustained growth.
Expansion → Increased Economic Output + Consumer Spending Increases + Stock Prices Rises
- Peak: This is the time when the business is at the peak of its production. Economic growth slows or stagnates. Govt starts fiscal and monetary restrictions. In this phase, the price of the stock is at its peak.
Peak →Slow Economic Growth + Consumer Spending Decreases + Stock Price Peaked
- Recession: This is a period of economic downfall. During a recession, cyclical stocks can experience significant declines as the demand for products and services evaporates. Stock price starts falling.
Recession → Lower Economic Output + Consumer Spending Decreases + Stock Price Falls
- Trough: This is the lowest point for any business when there is enough supply of product but no demand. The stock price is at its lowest level. In response, the government may implement fiscal policies to stimulate the economy. It’s a transitional period when the economic decline stops and recovery begins.
Trough → No Growth + No Spending + Stock Price Bottomed

Income Stocks

Income stocks are the stocks that provide regular income in the form of dividends to their investors. These businesses distribute a portion of profits to its shareholders. These companies are often mature, well-established, and have a stable track record of profitability.
Characteristics of income stocks:
- Purpose: Regular passive income.
- Cashflows are reliable and predictable.
- These stocks have low exposure to risk.
- These stocks give moderate returns over the year.
- The pace of growth is low-moderate.
- Consistent increase in dividend payouts
Example
Coca-Cola (KO) – The company has paid dividends to its investors for over 100 years.
Value Stocks
Value stocks are shares in companies considered undervalued by the market. These companies usually have a low price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio or price-to-book (P/B) ratio, indicating that the stock is priced lower than its intrinsic value.
Characteristics of value stocks:
- In this investment strategy, an investor buys a high-quality stock at a lower price than its intrinsic value.
- The stocks provide a margin of safety
- These stocks have solid fundamentals and promising numbers, making them investors friendly.
- Usually called bargained prices
- Most likely pay dividends
- High research required
Growth Stocks

Growth stocks are shares of companies that are expected to grow faster than the overall market.
A company uses its profit for two purposes.
- Distributes to its shareholder as a dividend or
- Retains these earnings for re-investment in the company.
Usually, stocks of companies that re-invest all or most of their profit in the company’s progress are called growth stocks.
Characteristics of growth stock:
- These stocks focus more on the expansion and growth of the company. The growth of these companies is faster than the average growth of other companies in the same industry.
- The risk involved in these stocks is high
- If the stock performs well, they yield excellent returns to investors leading to massive wealth accumulation.
- Growth stocks have high price-to-earnings ratios (P/E ratios) because investors are willing to pay more for the potential of future earnings growth.
- Growth stocks are more volatile
Example
Amazon re-invests its profits for growth and expansion. Thus, it is categorized into growth stocks.
Blue Chip Stock
Blue chip stocks are shares of large, well-established companies with a long history of reliable earnings and stable growth. These companies are typically leaders in their industry and have a reputation for consistent performance.
Characteristics of blue chip companies:
- They have a long history of operations
- Stocks are financially strong
- Generally, they have a large market capitalization
- The companies are known for offering high-quality products and services
- They are often market leaders
Example
Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) – A healthcare company that develops, manufactures and sells pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and consumer healthcare products.
The S&P 500 includes many blue chip companies, as they are typically large,
Sector Stocks
Every stock belongs to a particular sector. A sector is a grouping of companies involved in similar types of businesses, such as technology, healthcare, energy, or consumer goods.
The GICS framework
The GICS (Global Industry Classification Standard), is a system developed by MSCI. The GICS structure comprises 11 sectors, 24 industry groups, 69 industries, and 158 subindustries.
Here are some examples of companies that fall under 11 sector stocks:
Communication services:
- Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL)
- Facebook Inc. (FB)
- Netflix Inc. (NFLX)
- Walt Disney Co. (DIS)
Consumer discretionary:
- Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN)
- Nike Inc. (NKE)
- Starbucks Corp. (SBUX)
- Tesla Inc. (TSLA)
Consumer staples:
- Coca-Cola Co. (KO)
- Procter & Gamble Co. (PG)
- Walmart Inc. (WMT)
- McDonald’s Corp. (MCD)
Energy:
- Chevron Corp. (CVX)
- Exxon Mobil Corp. (XOM)
- ConocoPhillips (COP)
- Schlumberger Ltd. (SLB)
Financials:
- JPMorgan Chase & Co. (JPM)
- Bank of America Corp. (BAC)
- Wells Fargo & Co. (WFC)
- Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (BRK.A)
Health care:
- Johnson & Johnson (JNJ)
- Pfizer Inc. (PFE)
- UnitedHealth Group Inc. (UNH)
- AbbVie Inc. (ABBV)
Industrials:
- Boeing Co. (BA)
- General Electric Co. (GE)
- Honeywell International Inc. (HON)
- 3M Co. (MMM)
Information technology:
- Apple Inc. (AAPL)
- Microsoft Corp. (MSFT)
- Intel Corp. (INTC)
- Advanced Micro Devices Inc. (AMD)
Materials:
- Dow Inc. (DOW)
- Ecolab Inc. (ECL)
- DuPont de Nemours Inc. (DD)
- Freeport-McMoRan Inc. (FCX)
Real estate:
- American Tower Corp. (AMT)
- Prologis Inc. (PLD)
- Simon Property Group Inc. (SPG)
- AvalonBay Communities Inc. (AVB)
Utilities:
- NextEra Energy Inc. (NEE)
- Dominion Energy Inc. (D)
- Duke Energy Corp. (DUK)
- Southern Co. (SO)
Who can Invest in sector stocks?
- Investors who have done extensive research on particular sectors and stocks of these sectors
- Investors who can predict and estimate future sectoral demand.
